- #1
caters
- 229
- 9
I was wondering if it is possible to have a breathable atmosphere at a sea level pressure of 6 atm(in other words, 6 times Earth's sea level atmospheric pressure).
Why am I asking this?
Well I know that above 5.11 atm, CO2 is past its triple point and thus it will become a liquid instead of going straight into a gas. Since at the critical point, the temperature is 31.1 degrees C and the pressure is 73 atm, this gives a wide range of temperatures and pressures for liquid CO2. Here is the phase diagram:
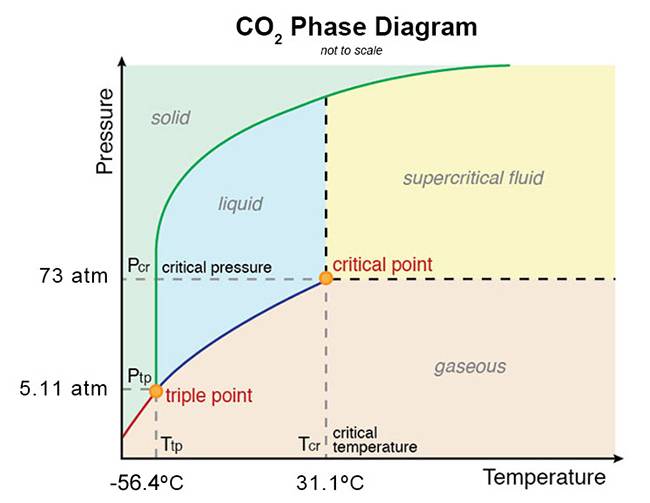
At 6 atmospheres the CO2 will be liquid between -56.4 and -53 degrees C. So during the winter at the poles, there could be temporary CO2 lakes as the CO2 rains out of the sky. I see no problem with bacteria evolving to thrive in CO2 lakes and become spores when there either is too little CO2 or the temperature gets too hot or too cold for liquid CO2. After all, bacteria on our planet have evolved to thrive at extremes of hot and cold, extremely anaerobic environments, etc.
This could be a natural process against global warming because then you have less CO2 each year than would be predicted simply by adding emitted CO2 to pre-existing CO2 because that extra CO2 would be sequestered by the bacteria in CO2 lakes at the poles and also by plants and photosynthetic bacteria in temperate and tropical climates
But back to my question. Is it possible to have a breathable atmosphere at a sea level pressure of 6 atm or is that air pressure simply too high to be breathable, even with an Earth life compatible percentage range of gases?
Why am I asking this?
Well I know that above 5.11 atm, CO2 is past its triple point and thus it will become a liquid instead of going straight into a gas. Since at the critical point, the temperature is 31.1 degrees C and the pressure is 73 atm, this gives a wide range of temperatures and pressures for liquid CO2. Here is the phase diagram:
At 6 atmospheres the CO2 will be liquid between -56.4 and -53 degrees C. So during the winter at the poles, there could be temporary CO2 lakes as the CO2 rains out of the sky. I see no problem with bacteria evolving to thrive in CO2 lakes and become spores when there either is too little CO2 or the temperature gets too hot or too cold for liquid CO2. After all, bacteria on our planet have evolved to thrive at extremes of hot and cold, extremely anaerobic environments, etc.
This could be a natural process against global warming because then you have less CO2 each year than would be predicted simply by adding emitted CO2 to pre-existing CO2 because that extra CO2 would be sequestered by the bacteria in CO2 lakes at the poles and also by plants and photosynthetic bacteria in temperate and tropical climates
But back to my question. Is it possible to have a breathable atmosphere at a sea level pressure of 6 atm or is that air pressure simply too high to be breathable, even with an Earth life compatible percentage range of gases?
