- #1
Pushoam
- 962
- 51
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
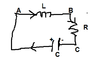
LCR circuit, calculating R when frequency width is given
Applying Kirchoff Voltage Loop Law,
## V_A – V_B + V_B - V_C + V_C – V_A = 0 ## ...(2)
## V_A – V_B ## is potential drop across inductor. Since current is flowing from A to B, I tend to take ## V_A > V_B ## . This way I am taking inductor as a resistor. Inductor has a very low resistance. So, ## V_A – V_B ## , taking this way is negligible.
Since the current is decreasing through inductor, there will be an EMF across it. This EMF will tend to increase the current according to Lenz's law. This EMF = - L ## \frac { dI} {dt} ## = ## V_A – V_B ## ...(3)
I doubt whether (3) is correct.
From (2) and (3),
- L ## \frac { dI} {dt} + IR - \frac { q} C = 0 ##
Is this correct?