- #1
JamesBennettBeta
- 10
- 1
mentor note: moved from ME forum hence no HW template.
Summary:: I am stuck into this problem for almost a week now. I think I solved it, but it seems something is wrong. Can someone point me, what is wrong here. It'll be so much helpful.
I am stuck into this problem for almost a week now. I think I solved it, but it seems something is wrong. Can someone point me, what is wrong here. It'll be so much helpful.
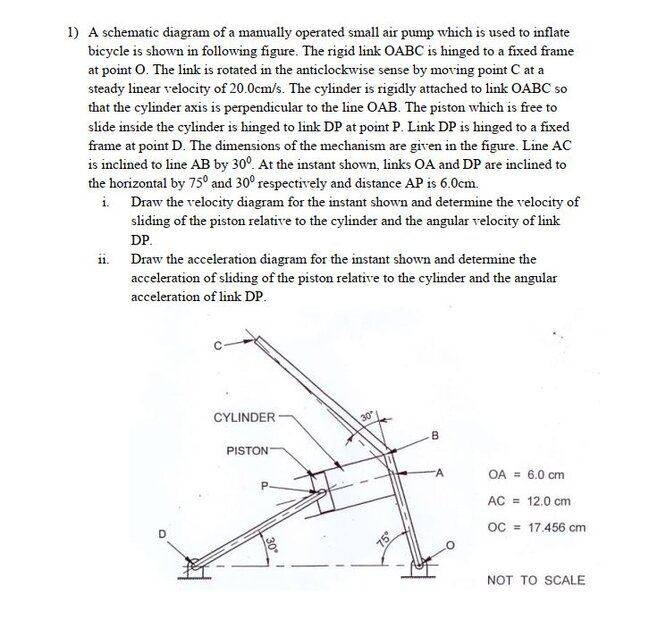
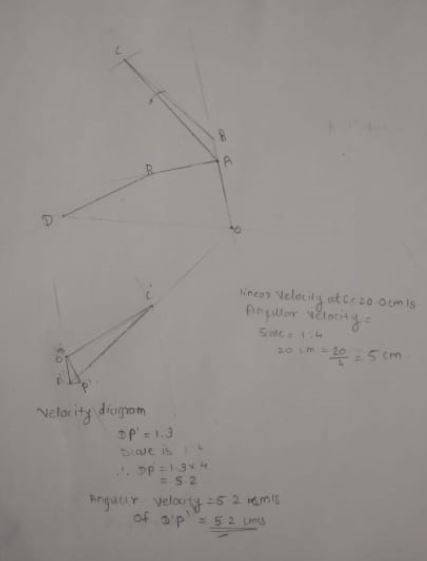
Summary:: I am stuck into this problem for almost a week now. I think I solved it, but it seems something is wrong. Can someone point me, what is wrong here. It'll be so much helpful.
I am stuck into this problem for almost a week now. I think I solved it, but it seems something is wrong. Can someone point me, what is wrong here. It'll be so much helpful.
Last edited by a moderator: