- #1
binbagsss
- 1,254
- 11
This is probably a stupid question but I have Neumann BC boundary : ## \nabla u . \vec{n} =0## (same for ##v##)conditions for the following reaction-diffusion system on a [0,L_1]x[0,L_2]x...x...[0,L_n] n times in n dimensional space so ##u=u(x_1,...,x_n,t)## is a scalar I believe?
so that ## \nabla u . \vec{n} ## is a vector times a vector is a scalar,my notes then say:
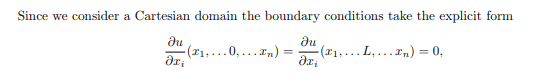 and so, I'm confused how to argue, from, a summation of ##u_i## derivatives we conclude that each ##u_i## derivative must individually be zero? unless we are specifying ##n## different normal vectors, one for each surface (divided by two for the what would be a negative of this normal vector) ? so like ##(1,0...0)## ,...,(0,0,...1) ##
and so, I'm confused how to argue, from, a summation of ##u_i## derivatives we conclude that each ##u_i## derivative must individually be zero? unless we are specifying ##n## different normal vectors, one for each surface (divided by two for the what would be a negative of this normal vector) ? so like ##(1,0...0)## ,...,(0,0,...1) ##
ahh this must be the case actually and i have misinterpreted the boundary condition?? thanks
so that ## \nabla u . \vec{n} ## is a vector times a vector is a scalar,my notes then say:
ahh this must be the case actually and i have misinterpreted the boundary condition?? thanks
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: