- #1
teunKeusters
- 3
- 0
Sorry if I didn't post this at the right place.
Hi all,
I have a problem that I am not able to solve. I hope you guys can help me! I am creating a suction cup to grab and lift an object with a flexible surface made of out silicone The suction cup is also made out of some sort of flexible material (not sure which yet).
I currently am considering two different models, both circular, but one is a ring, while the other one is more like a disk. Both models contain 8 holes in the top surface to create a vacuum. A cross-section of both:
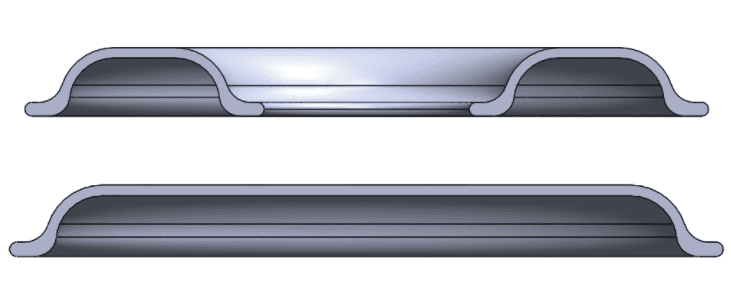
My question is: Which of the two models will stuck the best to the flexible surface, considering you are using the same pump. And which parameters are important for this question?
My reasoning so far:
On first instance you would expect the suction cup with the largest surface to pull with the largest force. However, when the silicone surface is sucked into the cup it will block the air holes. This probably limits the surface area to the surface of the 8 holes. My gut feeling is that more pressure is needed to make the silicone reach the top of the model in the ring model, but perhaps that is just nonsense.
I hope you guys can help me making sense of the choice I will eventually make. I tried to ask this question as clear as possible, but I have trouble formulating it, so if anything is unclear, pleas ask me.
Thanks in advance guys!
Hi all,
I have a problem that I am not able to solve. I hope you guys can help me! I am creating a suction cup to grab and lift an object with a flexible surface made of out silicone The suction cup is also made out of some sort of flexible material (not sure which yet).
I currently am considering two different models, both circular, but one is a ring, while the other one is more like a disk. Both models contain 8 holes in the top surface to create a vacuum. A cross-section of both:
My question is: Which of the two models will stuck the best to the flexible surface, considering you are using the same pump. And which parameters are important for this question?
My reasoning so far:
On first instance you would expect the suction cup with the largest surface to pull with the largest force. However, when the silicone surface is sucked into the cup it will block the air holes. This probably limits the surface area to the surface of the 8 holes. My gut feeling is that more pressure is needed to make the silicone reach the top of the model in the ring model, but perhaps that is just nonsense.
I hope you guys can help me making sense of the choice I will eventually make. I tried to ask this question as clear as possible, but I have trouble formulating it, so if anything is unclear, pleas ask me.
Thanks in advance guys!