- #1
Rahul Das Gupta
- 2
- 0
i am trying to figure out the relationship between diameter of a drop of liquid, its density and its shape. Can somebody explain to me the following two lines?
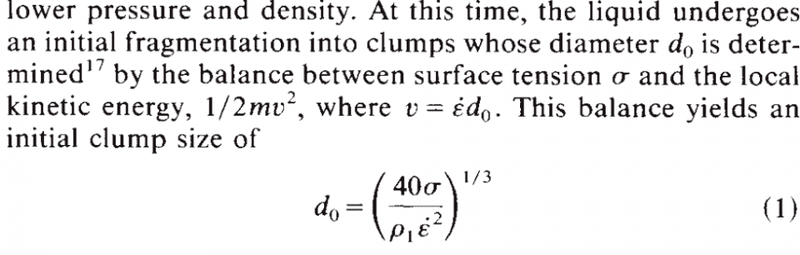
The melt drop radius, surface tension, and density are all related to one another through the Young-Laplace equation. This equation states that the pressure difference across a curved interface is directly proportional to the surface tension and inversely proportional to the radius of curvature. In other words, as the melt drop radius decreases, the surface tension increases, and the density also increases.
Surface tension is the force that causes the surface of a liquid to contract and behave like a stretched elastic membrane. In the case of a melt drop, the surface tension pulls the drop into a spherical shape, as this is the shape that minimizes surface area and therefore minimizes the surface tension. However, other factors such as gravity and intermolecular forces can also influence the shape of a melt drop.
Surface tension plays a crucial role in materials science, particularly in the fields of metallurgy and polymer science. It affects the wetting behavior of materials, the formation of bubbles and foams, and the stability and mechanical properties of materials. Understanding and controlling surface tension is essential for creating new materials and improving existing ones.
The surface tension of a material can be measured using various techniques, including the drop weight method, pendant drop method, and Wilhelmy plate method. These methods involve measuring the force required to deform or detach a droplet or film of the material, and then using mathematical equations to calculate the surface tension.
Yes, surface tension can be modified and controlled through various methods, such as adding surfactants or changing the temperature or pressure. Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension of a material by reducing the attractive forces between molecules at the surface. Changes in temperature and pressure can also affect the surface tension of a material, as they can alter the intermolecular forces between molecules.