- #1
Wilbert
- 1
- 0
MODERATOR NOTE: THIS IS A MISPLACED COURSEWORK THREAD, SO NO TEMPLATE WAS USED
I need help verifying the correct answers for the following questions.
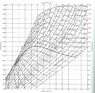
2. An ideal Rankine cycle is operated with a turbine inlet pressure of 500 psia and an inlet temperature of 600 oF. The steam is isentropically expanded through the turbine to 2 psia as shown in the following T-s diagram. Under these operating conditions, find the following .
(a) Using the Mollier diagram on page 9 of this exam, find the entropy at the turbine inlet and turbine outlet. Clearly identify the turbine inlet and outlet entropies on the given Mollier diagram.
I was given 1765 btu/R from another source
My Ans. 1.56 Btu/lb-R
(b) Using the Mollier diagram, find the enthalpy at the turbine inlet and turbine outlet. Clearly identify the turbine inlet and outlet enthalpies on the given Mollier diagram.
Another source 1560 BTu/lbm
My ans. h4=1300 BTu/lbm h5= 900 BTu/lbm
(c) Using the Mollier diagram , determine percent moisture of the steam at the turbine outlet.
another source 8%
My ans 22% (d) Using the steam tables, determine the enthalpy at the pump inlet and pump outlet (neglect pump work).
Work done by the pump is equal to w/pump = h2 - h1
since pump work has to be neglect h2 ≅ h1
Enthapy at inlet and outlet of pump is 89.575 Btu/lbm
(e) Using values obtained from part (a), part (b), and part (d), determine the cycle efficiency (neglect pump work)Efficiency = Net work done / Heat input cycle
395/1205 = 32.81%
(f) Determine the work output of the turbine.
W = h3 - h4 = 1300 -905 =395 Btu/lbm(g) Determine the heat rejected by the condenser.
Heat rejected by condenser = h4 - h1 = 905 -94 = 810 Btu/lbm(h) Determine the heat gain or heat added to the boiler.
Heat added to boiler = h3 - h3 = 1300 - 95.5 = 1204 btu/lbm
I need help verifying the correct answers for the following questions.
2. An ideal Rankine cycle is operated with a turbine inlet pressure of 500 psia and an inlet temperature of 600 oF. The steam is isentropically expanded through the turbine to 2 psia as shown in the following T-s diagram. Under these operating conditions, find the following .
(a) Using the Mollier diagram on page 9 of this exam, find the entropy at the turbine inlet and turbine outlet. Clearly identify the turbine inlet and outlet entropies on the given Mollier diagram.
I was given 1765 btu/R from another source
My Ans. 1.56 Btu/lb-R
(b) Using the Mollier diagram, find the enthalpy at the turbine inlet and turbine outlet. Clearly identify the turbine inlet and outlet enthalpies on the given Mollier diagram.
Another source 1560 BTu/lbm
My ans. h4=1300 BTu/lbm h5= 900 BTu/lbm
(c) Using the Mollier diagram , determine percent moisture of the steam at the turbine outlet.
another source 8%
My ans 22% (d) Using the steam tables, determine the enthalpy at the pump inlet and pump outlet (neglect pump work).
Work done by the pump is equal to w/pump = h2 - h1
since pump work has to be neglect h2 ≅ h1
Enthapy at inlet and outlet of pump is 89.575 Btu/lbm
(e) Using values obtained from part (a), part (b), and part (d), determine the cycle efficiency (neglect pump work)Efficiency = Net work done / Heat input cycle
395/1205 = 32.81%
(f) Determine the work output of the turbine.
W = h3 - h4 = 1300 -905 =395 Btu/lbm(g) Determine the heat rejected by the condenser.
Heat rejected by condenser = h4 - h1 = 905 -94 = 810 Btu/lbm(h) Determine the heat gain or heat added to the boiler.
Heat added to boiler = h3 - h3 = 1300 - 95.5 = 1204 btu/lbm
Attachments
Last edited: