- #1
Homakruz
- 5
- 0
Well, I took a Physics midterm this morning, I had a bit of trouble with a few of the questions and was hoping I could get some help here.
I did what I thought to be right, but as I really only started picking up physics concepts just recently, I am a bit weary on if I actually computed them correctly. I am just hoping someone can check my work as I don't have an answer key.
Hopefully there is no problem with having multiple questions on one topic.
One last thing, I am rewriting these questions from memory, so if something doesn't make much sense tell me and I will try and fix it.
Problem #1:
A .5kg ball is spun around a loop on a vertical plane by a 1.45m long massless string.
If the string tension is 15N, What is the speed of the mass when it is at the top of the loop(90 degrees)?
Relevant variables:
[tex]m = .5kg[/tex] || [tex]r = 1.45m[/tex] || [tex]T = 15N[/tex] || [tex]\theta = 90[/tex]
Relevant equations:
Newton's Second Law
Centripetal Acceleration
Solution Attempt:
[tex]F = ma[/tex]
[tex]T - W = ma[/tex]
[tex]T - mg = \frac{mv^2}{r}[/tex]
[tex]v^2 = \frac{r(T-mg)}{m}[/tex]
[tex]v = \sqrt{ r(T-mg)/m }[/tex]
[tex]v = \sqrt{ 1.45( 15 - 4.9 )/ .5 }[/tex]
[tex]v = 5.4 m/s[/tex]
On this on I am just a little unsure of, I feel like I am forgeting an force somewhere in the problem.
I just want to know if I went about this one correctly.
Problem #3:
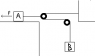
This one uses the attached figure, just to give you a visual representation of what I am explaining.
Again I am completely clueless on whether or not I subbed in the right equations here.
Box A is pulled on a frictionless surface by a force of 120N in the direction of the vector in the picture.
Both Box A and B weight 7 kg.
What is the tension in the rope holding block B?
Relevant variables:
[tex]m_a = m_b = 7kg[/tex]||[tex]F_p = 120N[/tex]||[tex]a_b = 2a_a[/tex]
Relevant equations:
Newton's Second Law
Solution Attempt:
=> Block B:
[tex]F = ma[/tex]
[tex]T - w = m_ba_b[/tex]
[tex]T = m_ba_b + m_bg[/tex]
[tex]T = m_b(a_b + g)[/tex]
=> Block A:
[tex]F = ma[/tex]
[tex]F_p - 2T = m_aa_a[/tex]
I used 2T here as a part of the force because of the pulley separating the ropes into 2 equal tension parts.
I don't know if I was supposed to use this or not, but it just makes sense to do so for me.
*Subbing in [tex]T[/tex] from Block B equation.
[tex]F - 2m_b(a_b + g) = m_aa_a[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_ba_b - 2m_bg = m_aa_a[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_bg = m_aa_a + 2m_ba_b[/tex]
*Subbing in [tex]2a_a[/tex] for [tex]a_b[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_bg = m_aa_a + 4m_ba_a[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_bg = a_a(4m_b + m_a)[/tex]
[tex]a_a = \frac{F - 2m_bg}{4m_b + m_a}[/tex]
[tex]a_a = \frac{120 - 2(7)(9.8)}{35}[/tex]
[tex]a_a = -.49 m/s[/tex]
[tex]a_b = -.98 m/s[/tex]
*Going back to Block B equation
[tex]T = 7( -.98 + 9.8 )[/tex]
[tex]T = 62 N[/tex]
Anyways, any help on these 3 problems would be much appreciated, especially on the last one.
Thanks in advance!
*One more on a post down, I couldn't fit it on this post.*
I did what I thought to be right, but as I really only started picking up physics concepts just recently, I am a bit weary on if I actually computed them correctly. I am just hoping someone can check my work as I don't have an answer key.
Hopefully there is no problem with having multiple questions on one topic.
One last thing, I am rewriting these questions from memory, so if something doesn't make much sense tell me and I will try and fix it.
Problem #1:
A .5kg ball is spun around a loop on a vertical plane by a 1.45m long massless string.
If the string tension is 15N, What is the speed of the mass when it is at the top of the loop(90 degrees)?
Relevant variables:
[tex]m = .5kg[/tex] || [tex]r = 1.45m[/tex] || [tex]T = 15N[/tex] || [tex]\theta = 90[/tex]
Relevant equations:
Newton's Second Law
Centripetal Acceleration
Solution Attempt:
[tex]F = ma[/tex]
[tex]T - W = ma[/tex]
[tex]T - mg = \frac{mv^2}{r}[/tex]
[tex]v^2 = \frac{r(T-mg)}{m}[/tex]
[tex]v = \sqrt{ r(T-mg)/m }[/tex]
[tex]v = \sqrt{ 1.45( 15 - 4.9 )/ .5 }[/tex]
[tex]v = 5.4 m/s[/tex]
On this on I am just a little unsure of, I feel like I am forgeting an force somewhere in the problem.
I just want to know if I went about this one correctly.
Problem #3:
This one uses the attached figure, just to give you a visual representation of what I am explaining.
Again I am completely clueless on whether or not I subbed in the right equations here.
Box A is pulled on a frictionless surface by a force of 120N in the direction of the vector in the picture.
Both Box A and B weight 7 kg.
What is the tension in the rope holding block B?
Relevant variables:
[tex]m_a = m_b = 7kg[/tex]||[tex]F_p = 120N[/tex]||[tex]a_b = 2a_a[/tex]
Relevant equations:
Newton's Second Law
Solution Attempt:
=> Block B:
[tex]F = ma[/tex]
[tex]T - w = m_ba_b[/tex]
[tex]T = m_ba_b + m_bg[/tex]
[tex]T = m_b(a_b + g)[/tex]
=> Block A:
[tex]F = ma[/tex]
[tex]F_p - 2T = m_aa_a[/tex]
I used 2T here as a part of the force because of the pulley separating the ropes into 2 equal tension parts.
I don't know if I was supposed to use this or not, but it just makes sense to do so for me.
*Subbing in [tex]T[/tex] from Block B equation.
[tex]F - 2m_b(a_b + g) = m_aa_a[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_ba_b - 2m_bg = m_aa_a[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_bg = m_aa_a + 2m_ba_b[/tex]
*Subbing in [tex]2a_a[/tex] for [tex]a_b[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_bg = m_aa_a + 4m_ba_a[/tex]
[tex]F - 2m_bg = a_a(4m_b + m_a)[/tex]
[tex]a_a = \frac{F - 2m_bg}{4m_b + m_a}[/tex]
[tex]a_a = \frac{120 - 2(7)(9.8)}{35}[/tex]
[tex]a_a = -.49 m/s[/tex]
[tex]a_b = -.98 m/s[/tex]
*Going back to Block B equation
[tex]T = 7( -.98 + 9.8 )[/tex]
[tex]T = 62 N[/tex]
Anyways, any help on these 3 problems would be much appreciated, especially on the last one.
Thanks in advance!
*One more on a post down, I couldn't fit it on this post.*