- #1
hidemi
- 208
- 36
- Homework Statement
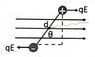
- The force exerted by a uniform electric field on a dipole is:
A. parallel to the dipole moment
B. perpendicular to the dipole moment
C. parallel to the electric field
D. perpendicular to the electric field
E. none of the above
The answer is E.
- Relevant Equations
- F = qE
I think the answe should be C as shown in the attachment.