- #1
ktw
- 8
- 2
- Homework Statement
- Whoops.. accidentally wrote everything in the solution box! Please see below.
- Relevant Equations
- Fx=0, Fy=0
Hi, I am a civil engineering student currently taking Statics. We are doing truss analysis in the class right now; and I know that this joint is marked as correct.
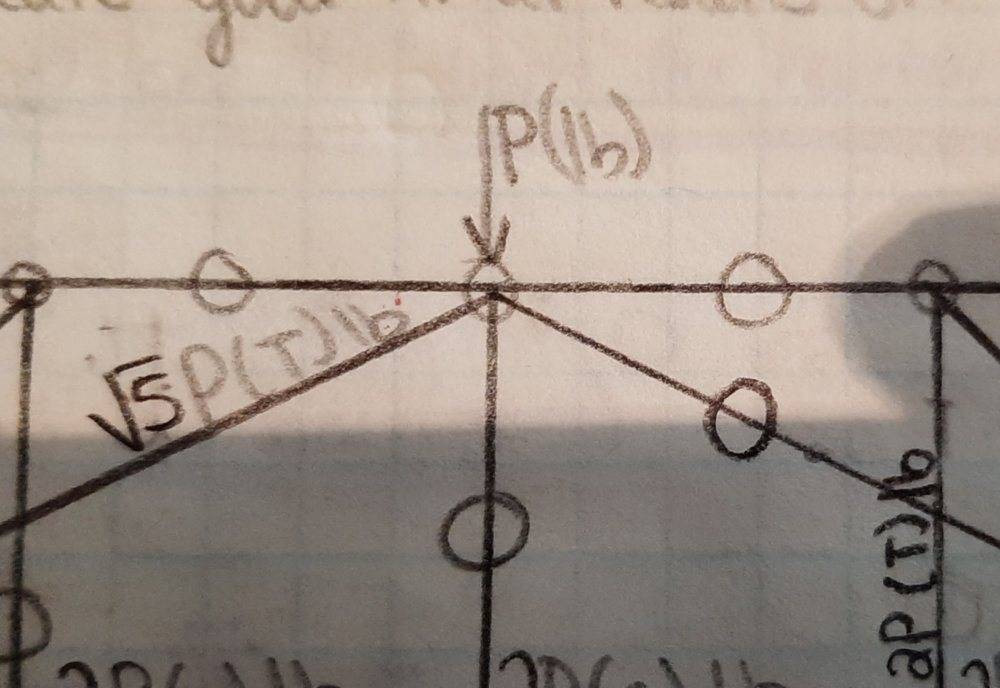
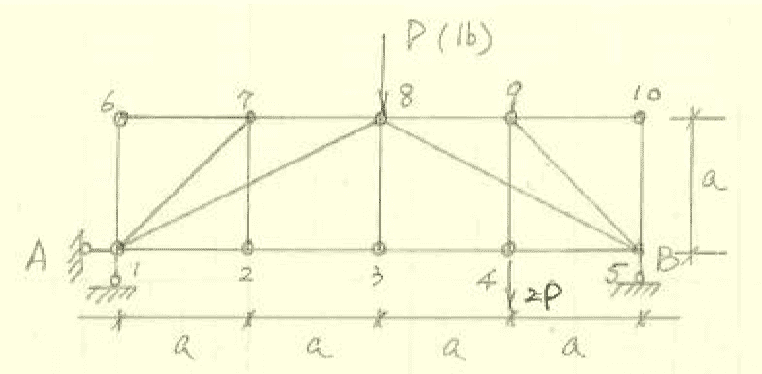
However, I don't see how this is even possible. I begin by considering this a concurrent 2D force system, Fy = 0 & Fx = 0. The equilibrium equation for Fy is -P + (1/√5)√5 * P + (1/√5)T = 0 ; where sin(θ) = (1/√5) and T is the diagonal that is following the line 8->5. I do not understand how the value of T can equal zero and then the member connecting joint 8 to joint 9 can also be zero; considering this would imply that (2/√5)√5P + 0 = 0 using the equilibrium equation Fx = 0. I understand zero force members and I do not think member 8->9 can be visually determined to be zero. Could anyone shed some light on this for me?
Thanks, Kyle
However, I don't see how this is even possible. I begin by considering this a concurrent 2D force system, Fy = 0 & Fx = 0. The equilibrium equation for Fy is -P + (1/√5)√5 * P + (1/√5)T = 0 ; where sin(θ) = (1/√5) and T is the diagonal that is following the line 8->5. I do not understand how the value of T can equal zero and then the member connecting joint 8 to joint 9 can also be zero; considering this would imply that (2/√5)√5P + 0 = 0 using the equilibrium equation Fx = 0. I understand zero force members and I do not think member 8->9 can be visually determined to be zero. Could anyone shed some light on this for me?
Thanks, Kyle
Last edited: