- #1
Althistorybuff
- 20
- 0
Question from an amateur:
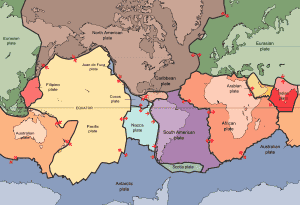
The Earth's plates seem pretty large compared to the planet. This example has about 20 to 30 with about 6 seemingly making up the majority of the Earth's surface.
Is there a reason why they are so large?
I'm writing a novel in which a planet, instead of having 20 to 30 plates, may have 100 small ones. That way, I don't have a handful of large oceans or large continents but a huge number of smaller Greenland to Hawaii sized island chains with dozens of large Mediterranean-sized seas.

Is there some aspect of planetary tectonics that would explain why there would be more numerous but smaller plates?
Thanks.
The Earth's plates seem pretty large compared to the planet. This example has about 20 to 30 with about 6 seemingly making up the majority of the Earth's surface.
Is there a reason why they are so large?
I'm writing a novel in which a planet, instead of having 20 to 30 plates, may have 100 small ones. That way, I don't have a handful of large oceans or large continents but a huge number of smaller Greenland to Hawaii sized island chains with dozens of large Mediterranean-sized seas.
Is there some aspect of planetary tectonics that would explain why there would be more numerous but smaller plates?
Thanks.