- #1
Gundam404
- 4
- 0
Homework Statement
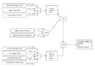
FIGURE 2 shows an improved arrangement for separating water from the hydrocarbon liquid for the process in question 2. Two simple level control loops, LC, have been added to regulate flow control valves on a pumped system. Extra protection is also provided in the form of high level alarms, LA, one to each side of a baffle plate fitted in the tank. It has been determined that estimating the probable frequency of hydrocarbon passing to the water drain will permit judgement as to whether this would be an acceptable risk. FIGURE 3 is the cause tree for this TOP event, showing the conventional 'AND' and 'OR' gates together with typical fail-to-danger fault frequencies for the control and alarm equipment, including estimates for electricity and instrument air failure. Also shown are probabilities (3%) for operator failure to respond to the alarm system which is rated at 97% reliable.
Hello,
I have attempted this question with several different outcomes. I have picked this answer currently and was wondering if anyone could please check it for me. All equations used are from the university literature but I feel like my numbers are wrong somewhere. Any help in the correct direction is appreciated.
Many thanks.
Homework Equations
AND gates are multiplied together.
OR gates are added together.
Fractional dead time (fdt) = 1/2 x T x F
T = Test Interval
F = Failure rate