- #1
Sid55
- 26
- 1
- TL;DR Summary
- Any suggestions on selecting correct voltage and current rating ?
I would like to add a Schottky diode on the output of a boost converter to stop reverse current flow that can handle DC 10-60V up to 12A on the output but with as little voltage drop as possible.
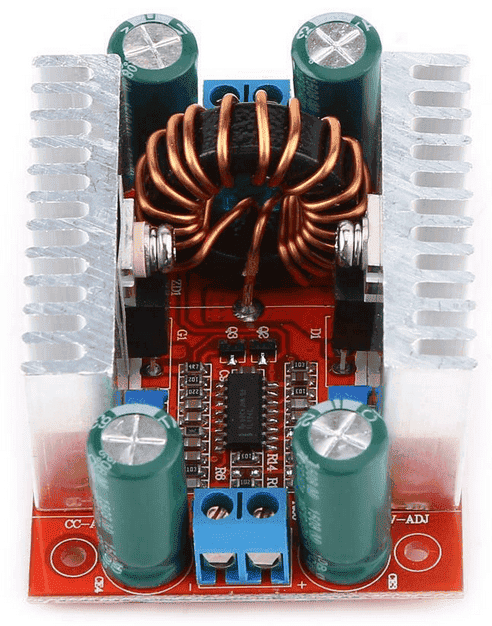
Non-isolated boost converter
Input Voltage: DC8.5V to 50V
Output Voltage: DC10V to 60V
Max. Ouput Current: 12A
Frequency: 150KHz
Input Voltage: DC8.5V to 50V
Output Voltage: DC10V to 60V
Max. Ouput Current: 12A
Frequency: 150KHz