- #1
etf
- 179
- 2
Here is my circuit:
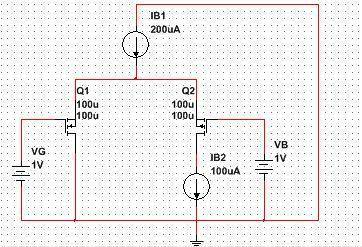
Q1 is NMOS and Q2 is PMOS.
Q1: VT1=0.7V, beta1=2mA/V^2
Q2: VT2=-0.9V, beta2=1.8mA/V^2.
I assumed that both transistors work in saturation. In this mode it must be:
Q1: VG1S1 > VT1, VG1D1 < VT1, ID1=beta1*(VG1S1-VT1)^2/2,
Q2: VS2G2 > -VT2, VD2G2 < -VT2, ID2=beta2*(VS2G2+VT2)^2/2.
We see on scheme that ID2=IB2. Using KCL we get ID1=IB1-ID2=100uA.
Using KVL we get VG1S1=VG. If we put VG1S1=VG in our equation for drain's current in saturation mode we get that ID1=9*10^(-5) A so our equation doesn't hold? (ID1=IB1-ID2=100uA.)
Q1 is NMOS and Q2 is PMOS.
Q1: VT1=0.7V, beta1=2mA/V^2
Q2: VT2=-0.9V, beta2=1.8mA/V^2.
I assumed that both transistors work in saturation. In this mode it must be:
Q1: VG1S1 > VT1, VG1D1 < VT1, ID1=beta1*(VG1S1-VT1)^2/2,
Q2: VS2G2 > -VT2, VD2G2 < -VT2, ID2=beta2*(VS2G2+VT2)^2/2.
We see on scheme that ID2=IB2. Using KCL we get ID1=IB1-ID2=100uA.
Using KVL we get VG1S1=VG. If we put VG1S1=VG in our equation for drain's current in saturation mode we get that ID1=9*10^(-5) A so our equation doesn't hold? (ID1=IB1-ID2=100uA.)
Last edited: