- #1
isison
- 10
- 0
Dear all,
I am simulation a lossy transmission line like this:
http://www.ece.uci.edu/docs/hspice/hspice_2001_2-2878.jpg
with G having zero conductance (open). So it is a standard lossy transmission line with RLC components. All R, L, and C values are the same, so there is no variation from segment to segment. There are total 1000 segments being simulated in HSPICE.
The input function is a step function that goes from low to high at t=0. I look at the propagation of this signal through the transmission line at a certain time. I obtained a voltage vs. position plot like this:
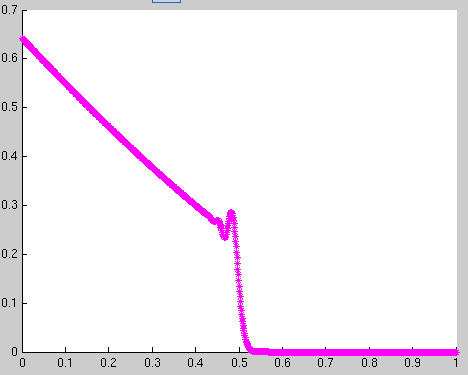
The x-axis is the position, and y-axis is the voltage sampled at each segment.
The general shape of this transient curve makes sense to me. It is step function signal front propagates toward right. However, there is this oscillation at the signal front that I seen unable to get rid of.
What is the physical reason behind this oscillation? It's best if you can explain this in a layman term to someone who is not familiar with transmission line analysis.
Thanks!

I am simulation a lossy transmission line like this:
http://www.ece.uci.edu/docs/hspice/hspice_2001_2-2878.jpg
with G having zero conductance (open). So it is a standard lossy transmission line with RLC components. All R, L, and C values are the same, so there is no variation from segment to segment. There are total 1000 segments being simulated in HSPICE.
The input function is a step function that goes from low to high at t=0. I look at the propagation of this signal through the transmission line at a certain time. I obtained a voltage vs. position plot like this:
The x-axis is the position, and y-axis is the voltage sampled at each segment.
The general shape of this transient curve makes sense to me. It is step function signal front propagates toward right. However, there is this oscillation at the signal front that I seen unable to get rid of.
What is the physical reason behind this oscillation? It's best if you can explain this in a layman term to someone who is not familiar with transmission line analysis.
Thanks!