- #1
Mzzed
- 67
- 5
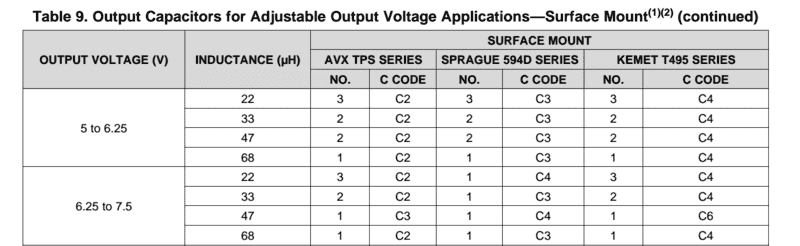
I have recently come across a datasheet for a buck converter regulator that uses the terms "c code" and "No." for certain capacitors but when going to the manufacturer datasheets for these capacitors they make no reference to any "c code" or one single number for a capacitor. If anyone could help me understand what these mean and how to find these specific capacitors from the manufacturers capacitor datasheet I would really appreciate it. The image bellow is where I have been reading these terms.