- #1
LT72884
- 323
- 48
- Homework Statement
- A ductile hot-rolled steel bar has a minimum yield strength in tension and compression of 350 MPa. Using the distortion-energy and maximum-shear-stress theories, determine the factors of safety for the following plane stress states.
σx = 100 MPa and σy = 100 MPa
- Relevant Equations
- NA
Hell
Our homework is done through mcgraw hill connect. I am able to see the solution to the problem and it contradicts what the book and powerpoint says.
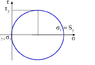
according to the powerpoint given by my professor, moors circle, sigma1 = Sy or yield strength. Powerpoint also states that sigma(x) is sigma1, sigma(y) is sigma2 and sigma(z) is sigma3.
If the powerpoint is correct, then there is no way that sigma(x) from the mcgraw hill assignment IS 100, because Sy is 350. The solution states sy is 350 as well. see attached file
n=sy/Tmax
Tmax we know is half of sy based on moors circle so 350/175 = n
view attached files to see what i mean

Our homework is done through mcgraw hill connect. I am able to see the solution to the problem and it contradicts what the book and powerpoint says.
according to the powerpoint given by my professor, moors circle, sigma1 = Sy or yield strength. Powerpoint also states that sigma(x) is sigma1, sigma(y) is sigma2 and sigma(z) is sigma3.
If the powerpoint is correct, then there is no way that sigma(x) from the mcgraw hill assignment IS 100, because Sy is 350. The solution states sy is 350 as well. see attached file
n=sy/Tmax
Tmax we know is half of sy based on moors circle so 350/175 = n
view attached files to see what i mean