- #1
Anchovy
- 99
- 2
I have questions regarding the 24 gauge bosons of the SU(5) model. I keep seeing this matrix popping up in the documents I'm reading with no real explanation of why:
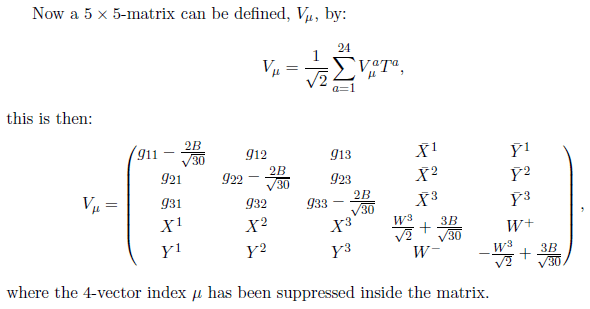
First of all I'm wondering how this is constructed, which means I'm wondering what the [itex]V_{\mu}^{a}[/itex] look like (I already have the 24 generators [itex]T^{a}[/itex]).
Actually what motivates me wanting to do this is that there are supposed to be 24 gauge bosons in this theory - the 12 of the standard model plus another 12. I can see the [itex]W^{\pm}[/itex],and also the [itex]W^{3}[/itex] and [itex]B[/itex] bosons are in there which mix to give the [itex]Z^{0}[/itex] and [itex]\gamma[/itex], so that accounts for 4 of the SM bosons. However, looking at the 3x3 in the top left of this matrix, I can see 9 [itex]g_{ij}[/itex] - but there are only supposed to be 8 gluons. So there's an extra g in there that I don't understand?
Furthermore, I've so far counted 4+9=13 bosons. There are supposed to be 24 so I need another 11 from somewhere but I only see 3 [itex]X^{i}[/itex] bosons and 3 [itex]Y^{i}[/itex] bosons, which gives another 6 (which is not enough, adding up to 19 bosons in total). Or if you count their antiparticles as a further 6 this gives 25 bosons, which is one too many. What is going on here?
Thanks.
First of all I'm wondering how this is constructed, which means I'm wondering what the [itex]V_{\mu}^{a}[/itex] look like (I already have the 24 generators [itex]T^{a}[/itex]).
Actually what motivates me wanting to do this is that there are supposed to be 24 gauge bosons in this theory - the 12 of the standard model plus another 12. I can see the [itex]W^{\pm}[/itex],and also the [itex]W^{3}[/itex] and [itex]B[/itex] bosons are in there which mix to give the [itex]Z^{0}[/itex] and [itex]\gamma[/itex], so that accounts for 4 of the SM bosons. However, looking at the 3x3 in the top left of this matrix, I can see 9 [itex]g_{ij}[/itex] - but there are only supposed to be 8 gluons. So there's an extra g in there that I don't understand?
Furthermore, I've so far counted 4+9=13 bosons. There are supposed to be 24 so I need another 11 from somewhere but I only see 3 [itex]X^{i}[/itex] bosons and 3 [itex]Y^{i}[/itex] bosons, which gives another 6 (which is not enough, adding up to 19 bosons in total). Or if you count their antiparticles as a further 6 this gives 25 bosons, which is one too many. What is going on here?
Thanks.