- #1
chuuke
- 3
- 1
Homework Statement
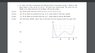
I'm trying to figure out how to do D) and relate time to this potential energy graph.
Homework Equations
All I really know is that F = -dU/dx
The Attempt at a Solution
I tried to do something with F = ma
and a = d2x/ dt2
and then set the - derivative of U(x) equal to the above equation
but I can't really get an answer, and am quite frustrated cause I don't know how to go about answering this.