- #1
JessicaHelena
- 188
- 3
Homework Statement
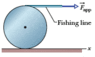
In the figure below, a constant horizontal force
(a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the center of mass of the cylinder?
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I'm confused... I feel like I could use torque — I could set the bottom point as the origin, and then tau_net = 18 x 2 x 0.11 + F_cm x 0.11.
However, I couldn't really get further than that and I am really confused. Could someone help me?