- #1
Jimmy87
- 686
- 17
When you look up a ray diagram for a telescope you get the following:
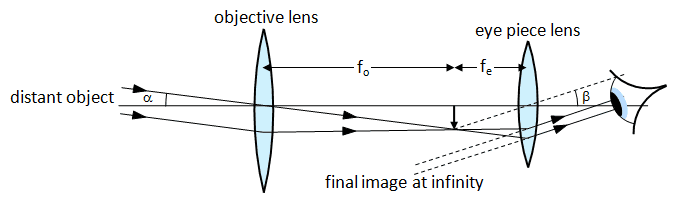
From reading my book it seems clear that the objective lens forms and image on the focal plane. This then serves as an image for the eyepiece. Since the focal length of the eyepiece at the focal length of the objective lens you get a virtual image at infinity. Three questions have come to me:1) I didn't think you could get an image at infinity since the light rays do not converge?
2) Different sources tell me different things about the focal lengths. This source says right at the beginning that for a telescope the focal lengths actually overlap:
3) I really don't get why the image from the objective lens is sometimes in the focal plane as oppose to the focal point. In the diagram above the light rays (although parallel) come in at some angle to the principle axis. When could this ever happen because surely you just point your telescope straight at the object you are looking at in the sky so that the rays will always be parallel to the principle axis? But then if they did am I right in saying that you would get no image as the rays would all converge to a point right at the focal point?
Thanks for any help given!
From reading my book it seems clear that the objective lens forms and image on the focal plane. This then serves as an image for the eyepiece. Since the focal length of the eyepiece at the focal length of the objective lens you get a virtual image at infinity. Three questions have come to me:1) I didn't think you could get an image at infinity since the light rays do not converge?
2) Different sources tell me different things about the focal lengths. This source says right at the beginning that for a telescope the focal lengths actually overlap:
3) I really don't get why the image from the objective lens is sometimes in the focal plane as oppose to the focal point. In the diagram above the light rays (although parallel) come in at some angle to the principle axis. When could this ever happen because surely you just point your telescope straight at the object you are looking at in the sky so that the rays will always be parallel to the principle axis? But then if they did am I right in saying that you would get no image as the rays would all converge to a point right at the focal point?
Thanks for any help given!