- #1
neildownonme
- 6
- 0
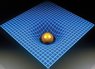
well yeah i understand that in general theory of relativity is about bending of space time. but why does the bending of spacetime itself is not relative? i mean look at these photos,
why does spacetime was bended that way? why not sidewards? why not on top?
just want to know why. thanks :)
why does spacetime was bended that way? why not sidewards? why not on top?
just want to know why. thanks :)
Attachments
Last edited: