- #1
andyrk
- 658
- 5
Homework Statement
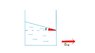
When a vessel containing a liquid is accelerated as shown in the attachment its surface slopes as shown, making an angle θ with the horizontal. Does this happen?
Homework Equations
Consider a differential mass element inside the liquid.
It experiences forces F1 and F2 in the right and the left direction respectively. Let its two sides have area A and be at depths h1 and h2 beneath the water surface. Then if we need to prove that why does the surface slope it is sufficient to prove that h1>h2 (This can only happen if the surface is sloped so that the distance from the water surface is not the same)
So :
F1 > F2 (As the differential element accelerates in the x direction the right side force has to be greater that the left side force)
=>F1/A > F2/A
=>P1>P2 (P1 and P2 are the pressures at the left and the right side of the differential element respectively)
=>h1ρg>h2ρg
=>h1>h2
My doubt was that what are the causes of F1 and F2?
Is it because of the cohesive forces? But aren't those forces attractive? So should the directions of the two forces F1 and F2 be opposite? So would that mean that the differential molecule is being pulled outside to expand? Really weird I know, but what causes both the forces?
Attachments
Last edited: