- #1
recreated
- 50
- 1
Glad it's Friday? I will be if you can help me with this :D :
I'm trying to understand an equation about calculating the power extracted by the blades of a wind turbine. I have spent a couple of hours going over it but still not making much more sense.
I'm trying to find out why P = 1/2*m*(v2 - v2d). Why the 1/2? Why the '-' sign?? And why the 2 ? I assume it is to do with F=ma, so the v (velocity) is squared to show acceleration but still I can't figure it all out.
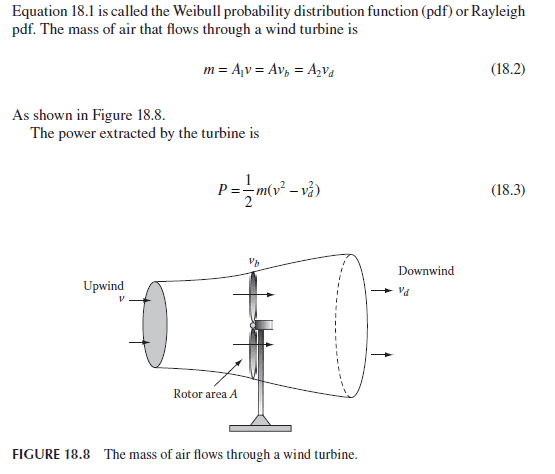
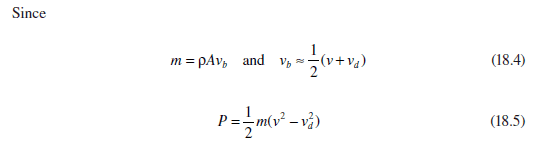
Any tips on how they got to the last equation (18.5) shown above would be amazing!
Thank you! Cannot wait for this to make sense
I'm trying to understand an equation about calculating the power extracted by the blades of a wind turbine. I have spent a couple of hours going over it but still not making much more sense.
I'm trying to find out why P = 1/2*m*(v2 - v2d). Why the 1/2? Why the '-' sign?? And why the 2 ? I assume it is to do with F=ma, so the v (velocity) is squared to show acceleration but still I can't figure it all out.
Any tips on how they got to the last equation (18.5) shown above would be amazing!
Thank you! Cannot wait for this to make sense