- #1
agnibho
- 46
- 0
Homework Statement
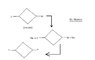
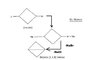
The problem given was to find out the resulting compound of this Wurtz reaction process using dry ether (Na).
Homework Equations
Now the main problem I faced was how to remove the Cl-atom and Br-atom. I am new to this so please help me out.
The Attempt at a Solution
I tried this out on my own. The dots are of course free electrons. Is this answer possible?? If not please help.