- #1
LCSphysicist
- 645
- 161
- Homework Statement
- All below
- Relevant Equations
- All below
See this figure:
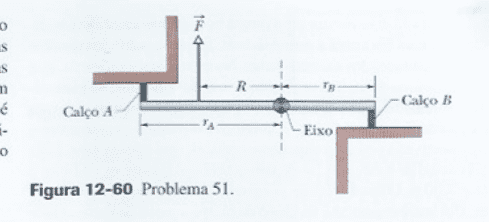
The rod is put at first between A and B shims without comprehension, suddenly a force is applied at R from an axis as the figure points. Find Fa and Fb. (the figure is a look from above)
This can be solved by consider the "constant elastic" of the shims equal, but my discussion is another.
The immediately wrong affirmation that F + Fb = Fa, if we try to apply this, it will lead us to wrong answers.
I am trying to analyse the consequences of this, this implies that immediately the center of mass is not at zero net force, so it has linear acceleration (it could be found, if we knew the mass), but this is a little tricky, that is, at what stage the forces net force will be zero? Or is this, or the rod will broken some time later the figure.
The rod is put at first between A and B shims without comprehension, suddenly a force is applied at R from an axis as the figure points. Find Fa and Fb. (the figure is a look from above)
This can be solved by consider the "constant elastic" of the shims equal, but my discussion is another.
The immediately wrong affirmation that F + Fb = Fa, if we try to apply this, it will lead us to wrong answers.
I am trying to analyse the consequences of this, this implies that immediately the center of mass is not at zero net force, so it has linear acceleration (it could be found, if we knew the mass), but this is a little tricky, that is, at what stage the forces net force will be zero? Or is this, or the rod will broken some time later the figure.