Discussion Overview
The discussion centers around the potential efficacy of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment for COVID-19, referencing a study by French doctor Didier Raoult. Participants explore the mechanisms by which these drugs might work, their historical uses, and the implications of the study's findings, while also addressing methodological concerns and alternative perspectives.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Exploratory
Main Points Raised
- Some participants note that hydroxychloroquine has established uses in treating lupus, rheumatic disorders, and malaria, while azithromycin is effective against certain bacterial infections, questioning the applicability of these effects to viral infections like COVID-19.
- One participant emphasizes that just because a drug works for one condition does not mean it will work for another, highlighting the differences between autoimmune diseases, bacterial infections, and viral infections.
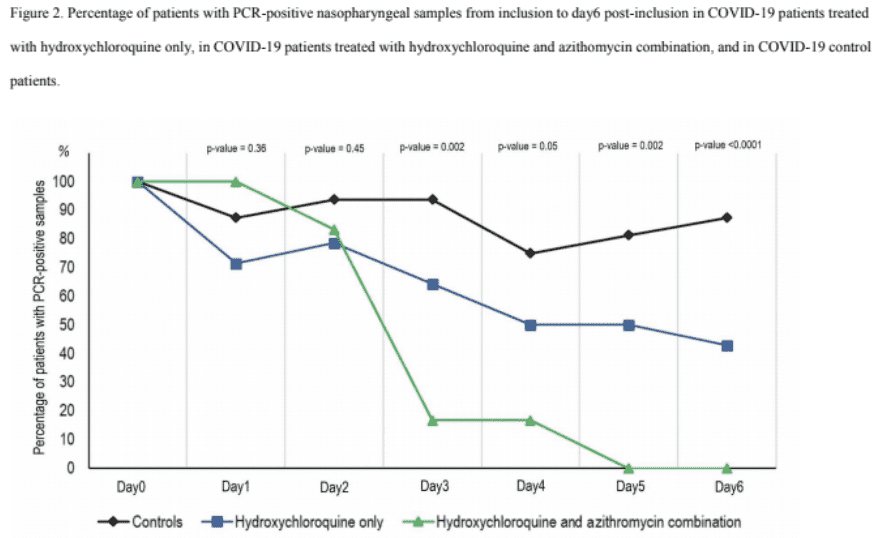
- Concerns are raised regarding the methodology of Raoult's study, including small sample sizes, lack of randomization, and the exclusion of certain patients from the analysis, which could skew results.
- Another participant mentions that a recent randomized trial from China suggests hydroxychloroquine may not be effective against COVID-19, contrasting with Raoult's findings.
- There is a discussion about the potential mechanisms of action for hydroxychloroquine and its effects on the immune system, with some proposing that the understanding of these mechanisms is still incomplete.
- Some participants argue that the limitations of the study do not negate the potential for hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to be effective, suggesting that further investigation is warranted.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express a range of opinions, with some supporting the potential of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin based on preliminary data, while others highlight significant methodological flaws and question the validity of the findings. There is no consensus on the efficacy of the treatment.
Contextual Notes
Limitations noted include the small sample size of the study, the lack of randomization, the absence of a placebo control, and the exclusion of patients from the analysis. These factors contribute to uncertainty regarding the reliability of the study's conclusions.