PhysicsRock
- 121
- 19
- Homework Statement
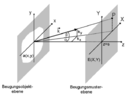
- Calculate the diffraction pattern for a 2D Fraunhofer-diffraction, where monochromatic and coherent light of wave length ##\lambda## (wave number ##\vec{k}=2\pi / \lambda \hat{n}##) falls onto a wall with two slits, located in the regions where ##9d \leq |x| \leq 10d##. Both slits span infinitely in the ##y##-direction.
- Relevant Equations
- ##\displaystyle E(k_x,k_y) \propto \int_{-\infty}^\infty \int_{-\infty}^\infty a(x,y) e^{-i(k_x x + k_y y)} dx dy##
##I(k_x,k_y) \propto E^2(k_x,k_y)##
My issue here is the fact that the slits are supposed to infinite in the ##y##-direction. With what's given in the assignment, I'd define the apparatus function ##a(x,y)## as
$$
a(x,y) = \begin{cases} 1 & , \, ( 9d \leq |x| \leq 10d ) \wedge (y \in \mathbb{R}) \\ 0 & , \, \text{else} \end{cases}
$$
Plugging this into the Fourier transform and only considering the ##y##-part of it yields
$$
F(k_x,k_y) \propto \int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{-i k_y y} dy.
$$
One recognizes this as the integral representation of the delta-distribution, with a conventional factor of ##2\pi##. That would mean that
$$
F(k_x,k_y) \propto 2 \pi \delta(k_y).
$$
I'm unsure whether this is what is to be expected or not. The interpretation would be that there is a single sharp peak when ##k_y## is not 0, and if it is, the ##x##-part takes over and results in an oscillation, as I would expect.
$$
a(x,y) = \begin{cases} 1 & , \, ( 9d \leq |x| \leq 10d ) \wedge (y \in \mathbb{R}) \\ 0 & , \, \text{else} \end{cases}
$$
Plugging this into the Fourier transform and only considering the ##y##-part of it yields
$$
F(k_x,k_y) \propto \int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{-i k_y y} dy.
$$
One recognizes this as the integral representation of the delta-distribution, with a conventional factor of ##2\pi##. That would mean that
$$
F(k_x,k_y) \propto 2 \pi \delta(k_y).
$$
I'm unsure whether this is what is to be expected or not. The interpretation would be that there is a single sharp peak when ##k_y## is not 0, and if it is, the ##x##-part takes over and results in an oscillation, as I would expect.