slakedlime
- 74
- 2
Hi :)
I have an A Level Mechanics 2 exam in 3 days. I managed to 'solve' this problem from my book, but I'm having some trouble with the underlying concepts. It would be really nice if someone could explain part (c) of the question to me (I've included my solution below but I don't understand how it works out). My book has next to no explanations and I'm self-studying for this exam, so I don't have access to any teachers either. Thank-you :)
A car of total mass 1200kg is traveling along a straight horizontal road at 40ms^-1 when the driver suddenly applies the brakes. The brakes exert a constant force and the car comes to rest after traveling a distance of 80m. The other resistances on the car total 500N.
(a) Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the brakes on the car.
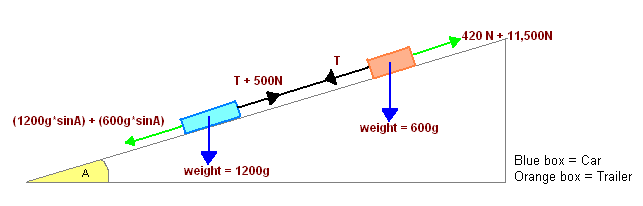
A trailer, with no brakes, is now attached to the car by means of a tow-bar. The mass of the trailer is 600kg, and when the trailer is moving, it experiences a constant resistance of magnitude 420N. The tow-bar is modeled as a light rod which remains parallel to the road at all times. The car and trailer come to a straight hill, which is inclined to the horizontal at an angle A, where sin A = 1/14. They move together down the hill. The driver suddenly applies the brakes, which exert a force of the same magnitude as before. The other resistances on the car remain at 500N.
(b) Find the deceleration of the car and the trailer when the brakes are applied.
(c) Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the car by the trailer when the brakes are applied.
* Power = Driving force x Speed
(a) Work done by the braking force to bring the car to rest
= Initial kinetic energy of the car
= 0.5 x 1200kg x (40ms^-1)^2
= 960,000 J
Now, (Braking force + Resistance) x Braking distance = Work done to bring the car to rest
or, (F + 500N) x 80 m = 960,000 J
Hence, F = 11,500N
(b) Combined decelerative force acting on the car and trailer
= (Resistance against trailer + Resistance against Car + Braking force) - (Vertical component of car's weight + Vertical component of trailer's weight)
= (420 + 500 + 11,500)N - (1200g*sinA + 600g*sinA)N
= 11,160N
Deceleration
= 11,160N/Mass of trailer + car
= 6.2 ms^-2
(c) Force exerted on the car by the trailer when brakes are applied
= The portion of the total decelerative force acting on the trailer
Either
= 11,160N/3 = 3,720N
(i.e. the portion of the total decelerative force acting on the trailer is in proportion to its mass)
Or
= Mass x Deceleration
= 6.2ms^-2 x 600kg
= 3,720N
Is this correct? It matches my book's answer of 3,700N. I have to mention that I don't understand the logic behind the answer. It luckily came to me while I was randomly trying out a range of possibilities (most were wrong). Could someone please explain how the answer works out? Why is the decelerative force acting on the trailer in proportion to its mass? Why doesn't the whole 11,160N act on the trailer?
I have an A Level Mechanics 2 exam in 3 days. I managed to 'solve' this problem from my book, but I'm having some trouble with the underlying concepts. It would be really nice if someone could explain part (c) of the question to me (I've included my solution below but I don't understand how it works out). My book has next to no explanations and I'm self-studying for this exam, so I don't have access to any teachers either. Thank-you :)
Homework Statement
A car of total mass 1200kg is traveling along a straight horizontal road at 40ms^-1 when the driver suddenly applies the brakes. The brakes exert a constant force and the car comes to rest after traveling a distance of 80m. The other resistances on the car total 500N.
(a) Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the brakes on the car.
A trailer, with no brakes, is now attached to the car by means of a tow-bar. The mass of the trailer is 600kg, and when the trailer is moving, it experiences a constant resistance of magnitude 420N. The tow-bar is modeled as a light rod which remains parallel to the road at all times. The car and trailer come to a straight hill, which is inclined to the horizontal at an angle A, where sin A = 1/14. They move together down the hill. The driver suddenly applies the brakes, which exert a force of the same magnitude as before. The other resistances on the car remain at 500N.
(b) Find the deceleration of the car and the trailer when the brakes are applied.
(c) Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the car by the trailer when the brakes are applied.
Homework Equations
* Power = Driving force x Speed
The Attempt at a Solution
(a) Work done by the braking force to bring the car to rest
= Initial kinetic energy of the car
= 0.5 x 1200kg x (40ms^-1)^2
= 960,000 J
Now, (Braking force + Resistance) x Braking distance = Work done to bring the car to rest
or, (F + 500N) x 80 m = 960,000 J
Hence, F = 11,500N
(b) Combined decelerative force acting on the car and trailer
= (Resistance against trailer + Resistance against Car + Braking force) - (Vertical component of car's weight + Vertical component of trailer's weight)
= (420 + 500 + 11,500)N - (1200g*sinA + 600g*sinA)N
= 11,160N
Deceleration
= 11,160N/Mass of trailer + car
= 6.2 ms^-2
(c) Force exerted on the car by the trailer when brakes are applied
= The portion of the total decelerative force acting on the trailer
Either
= 11,160N/3 = 3,720N
(i.e. the portion of the total decelerative force acting on the trailer is in proportion to its mass)
Or
= Mass x Deceleration
= 6.2ms^-2 x 600kg
= 3,720N
Is this correct? It matches my book's answer of 3,700N. I have to mention that I don't understand the logic behind the answer. It luckily came to me while I was randomly trying out a range of possibilities (most were wrong). Could someone please explain how the answer works out? Why is the decelerative force acting on the trailer in proportion to its mass? Why doesn't the whole 11,160N act on the trailer?