Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the calculation of volume generated by rotating a curve, specifically focusing on the integrand used in the volume formula. Participants explore the implications of using different exponential functions in the integral.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation, Debate/contested, Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
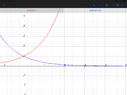
- One participant presents an integral involving \(e^x\) but is challenged on its validity due to the unbounded nature of the volume.
- Another participant suggests that using \(e^{-x}\) would yield a correct answer, leading to a bounded volume calculation.
- Multiple participants calculate the volume using \(e^{-2x}\) and arrive at the same result of \(\dfrac{\pi}{2}\), indicating a consensus on this specific calculation.
- There is a discussion about a potential typo in the problem statement, with some participants questioning why the function is negative and suggesting that \(e^{-2x}\) is the appropriate function to use.
- Participants express acknowledgment of each other's contributions, particularly in identifying the correct function to use in the volume calculation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is general agreement on the use of \(e^{-x}\) and \(e^{-2x}\) for bounded volume calculations, but disagreement remains regarding the initial function presented and its implications for the volume being unbounded.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the importance of the function's behavior on the interval \([0, \infty)\) and the implications of squaring the radius in the volume formula. There is an acknowledgment of missing assumptions regarding the problem statement.