Homework Help Overview
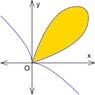
The discussion revolves around finding the area of a loop defined by the equation \(x^5+y^5=3x^2y^2\) in the x-y plane. Participants explore the use of polar coordinates and various integrals to express the area, while also considering the geometric properties of the curve.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Mathematical reasoning, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss expressing the area in polar coordinates, questioning the limits of integration and the form of the integrand. There is also exploration of different substitutions and simplifications for the radius \(r\) in terms of \(\theta\). Some participants express uncertainty about the complexity of the integrals involved.
Discussion Status
The discussion includes various attempts to derive the area, with some participants suggesting different methods and substitutions. There is acknowledgment of the complexity of the integrals, and while some participants report finding a numerical result for the area, there is no explicit consensus on a single method or solution.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the need for clarity on the curve's appearance and the appropriateness of the chosen limits and integrands. There are also references to potential typos and corrections in mathematical expressions, indicating ongoing refinement of the discussion.