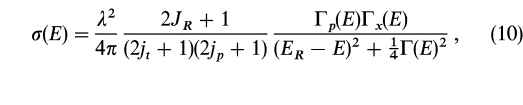SUMMARY
The Breit-Wigner formula describes the interaction between an incident particle and a nucleus, specifically highlighting how the probability of absorption increases when the energy of the incident particle resonates with the energy state of the nucleus. This resonance occurs around a specific energy level, denoted as ER, and is characterized by a finite width in energy, indicating the range of energies over which the resonance is effective. The discussion clarifies that this concept is analogous to electron orbitals, where nucleons (protons and neutrons) possess discrete energy states.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of quantum mechanics principles
- Familiarity with nuclear physics concepts
- Knowledge of resonance phenomena in particle interactions
- Basic grasp of energy states and their significance in atomic structure
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Breit-Wigner formula in detail
- Explore resonance theory in nuclear and particle physics
- Investigate the role of energy states in quantum mechanics
- Learn about applications of the Breit-Wigner formula in experimental physics
USEFUL FOR
Students and researchers in physics, particularly those focusing on nuclear and particle physics, as well as educators looking to explain resonance phenomena and the Breit-Wigner formula in their curriculum.