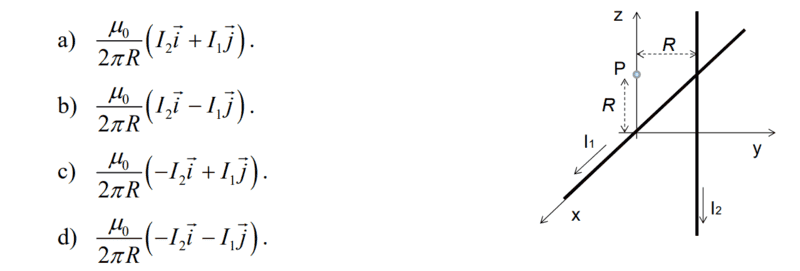SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the magnetic field at point P (0, 0, R) due to two perpendicular current-carrying wires. The first wire, aligned with the X-axis, carries a current I1 in the positive x-direction, while the second wire, parallel to the Z-axis, carries a current I2 downward. The magnetic field at point P can be determined using the Biot-Savart Law and the Right-Hand Rule to establish the direction of the magnetic field vectors generated by each wire. Participants are encouraged to show their calculations and reasoning for clarity.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Biot-Savart Law
- Familiarity with the Right-Hand Rule for magnetic fields
- Basic knowledge of vector addition
- Concept of magnetic field lines and their direction
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Biot-Savart Law in detail for magnetic field calculations
- Practice applying the Right-Hand Rule to various current configurations
- Explore vector addition techniques for combining magnetic fields
- Investigate the effects of varying current magnitudes on magnetic field strength
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in electromagnetism and magnetic field calculations related to current-carrying conductors.