sgvaibhav
- 65
- 0
Hi.
I am solving some questions on transformations of stress and strain.
I am getting stuck in one part of the question in all the problems.
I am having difficulties to determine σx, σy, τxy at a certain point in the structure.
Equations
σ = P/A + Mc/I
τ = Tc/J + VQ/It
Some components, or the entire stress can be zero depending on the question.
I will post one of the example questions where i am facing difficulty.
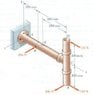
Question) [Picture attached] Several forces are applied to the pipe assembly shown. Knowing that the inner and outer diameters of the pipe are equal to 38 mm and 42 mm, respectively, determine (a) the principal planes and the principal stresses at point H located at the top of the outside surface of the pipe, (b) the maximum shearing stress at the same point.
My Difficulty - I know how to do the most of the question EXCEPT - finding σx, σy, τxy at a point H and/or point K.
Working- [ I think it should be correct]
Fx=0
Fy=0
Fz=0
Mx=T=-200x200mm = 40N.m
My=-200x300mm = 60N.m
Mz=48N.m
Next step find σx, σy and τxy at point H in this case.
After finding the stresses, i can solve the rest of the question.
Please share resources, or links to the concept of finding stresses if you are short of time.
I am solving some questions on transformations of stress and strain.
I am getting stuck in one part of the question in all the problems.
I am having difficulties to determine σx, σy, τxy at a certain point in the structure.
Equations
σ = P/A + Mc/I
τ = Tc/J + VQ/It
Some components, or the entire stress can be zero depending on the question.
I will post one of the example questions where i am facing difficulty.
Question) [Picture attached] Several forces are applied to the pipe assembly shown. Knowing that the inner and outer diameters of the pipe are equal to 38 mm and 42 mm, respectively, determine (a) the principal planes and the principal stresses at point H located at the top of the outside surface of the pipe, (b) the maximum shearing stress at the same point.
My Difficulty - I know how to do the most of the question EXCEPT - finding σx, σy, τxy at a point H and/or point K.
Working- [ I think it should be correct]
Fx=0
Fy=0
Fz=0
Mx=T=-200x200mm = 40N.m
My=-200x300mm = 60N.m
Mz=48N.m
Next step find σx, σy and τxy at point H in this case.
After finding the stresses, i can solve the rest of the question.
Please share resources, or links to the concept of finding stresses if you are short of time.