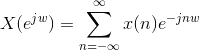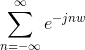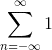SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) of the constant function 1. Participants clarify that the DTFT diverges for all values of ω except for integer multiples of 2π, where it converges to a Dirac delta function representation. Specifically, at ω = 0, the DTFT results in an infinite value, while for ω not equal to 2πk (where k is an integer), the DTFT converges to 0. The conversation emphasizes the importance of understanding geometric series and the properties of the Dirac delta function in this context.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
- Familiarity with geometric series and their convergence
- Knowledge of Dirac delta function and its properties
- Basic concepts of signal processing and distributions
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of the Dirac delta function in signal processing
- Learn about the convergence criteria for geometric series
- Explore the relationship between DTFT and inverse DTFT
- Investigate the application of Fubini's and Tonelli's theorems in sums and integrals
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in signal processing, electrical engineering, and applied mathematics who are working with Fourier transforms and need to understand the nuances of DTFT calculations.