SUMMARY
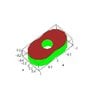
The volume of a double-lobed cam modeled by the inequalities \(\frac{1}{4} \leq r \leq \frac{1}{2}(1 + \cos 2\theta)\) and \(-\frac{9}{4(x^2 + y^2 + 9)} \leq z \leq \frac{9}{4(x^2 + y^2 + 9)}\) can be calculated using polar coordinates. The integration involves evaluating the double integral \(\iint_R (z_{upper} - z_{lower}) \, dA\) with bounds for \(r\) from \(\frac{1}{4}\) to \(\frac{1}{2}(1 + \cos 2\theta)\) and \(\theta\) from \(0\) to \(2\pi\). The calculated volume is approximately 0.79993, which is reasonable given the dimensions of the cam.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of double integrals in calculus
- Familiarity with polar coordinates and their conversion
- Knowledge of inequalities and their application in volume calculations
- Basic proficiency in using calculators for integration
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of double integrals in polar coordinates
- Learn about volume calculations using inequalities in three-dimensional space
- Explore advanced integration techniques, including numerical integration methods
- Investigate the geometric interpretation of volumes in polar coordinates
USEFUL FOR
Students in calculus, engineers working with mechanical designs, and anyone involved in geometric modeling or volume calculations in three-dimensional space.