- #1
squareroot
- 76
- 0
Hello.
I fail to follow one step in the process of calculating ⟨la∥Y(L)∥lb⟩ .
The spherical harmonics Yma(L)(r) represent the 2L+1 components of the spherical tensor of rank L. Writing the Eckart-Wigner th. for M = 0 yields:
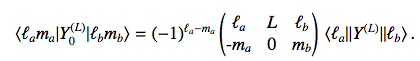 (1)
(1)
Also one can write
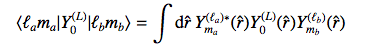 (2)
(2)
Coupling L and lb to l:
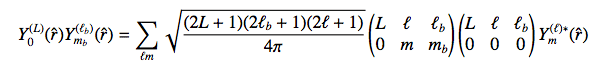 (3)
(3)
Thus having
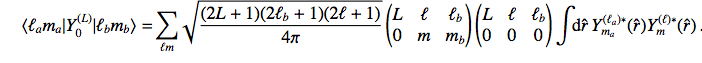 (4)
(4)
Now solving the integral:
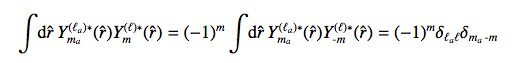 (5)
(5)
So:
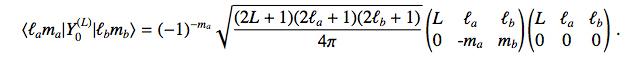 (6)
(6)
Here is my problem! After solving the integral (5) and replacing it into (4) I don't understand how that changes the Wigner 3j symbols from
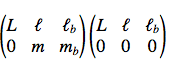 (3) into
(3) into
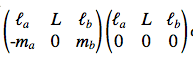 (6)
(6)
Could anyone please help me with this step? I m guessing it has something to do with does kronecker deltas from solving the integral and they act on the wigner symbols after substitution... but i have no idea how!
I fail to follow one step in the process of calculating ⟨la∥Y(L)∥lb⟩ .
The spherical harmonics Yma(L)(r) represent the 2L+1 components of the spherical tensor of rank L. Writing the Eckart-Wigner th. for M = 0 yields:
Also one can write
Coupling L and lb to l:
Thus having
Now solving the integral:
So:
Here is my problem! After solving the integral (5) and replacing it into (4) I don't understand how that changes the Wigner 3j symbols from
Could anyone please help me with this step? I m guessing it has something to do with does kronecker deltas from solving the integral and they act on the wigner symbols after substitution... but i have no idea how!