- #1
titansarus
- 62
- 0
- Homework Statement
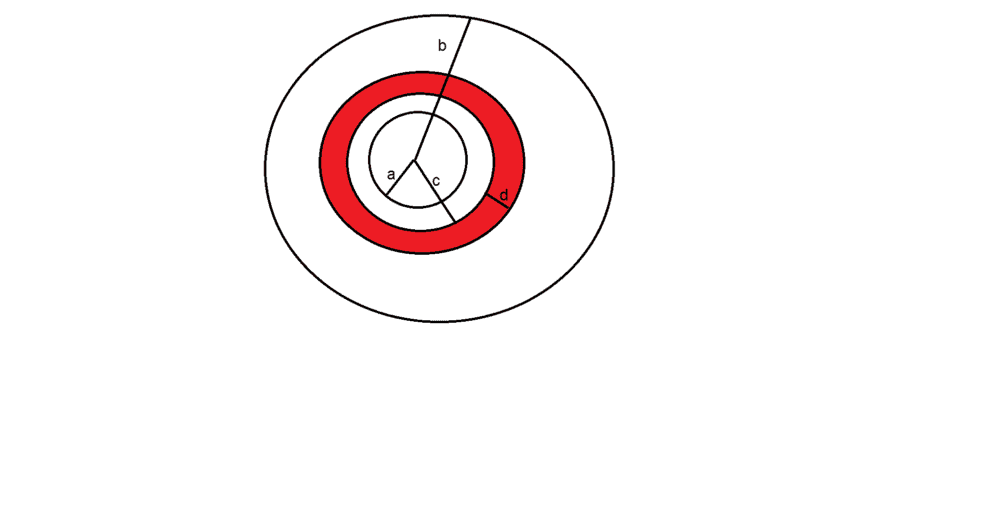
- We have two conductor spherical shells with radius ##a## and ##b## with charges +Q and -Q and a dielectric ##k## with thickness ##d## is put in distance ##c## from the center. (As in the picture
I) Find the Capacitance of capacitor?
II) Find the induced charge inside dielectric in a position with radial distance$r$ where $c<r<c+d$
- Relevant Equations
- ##C = Q/V , V =-\int E.ds ##
I) For the first part I used:
##V = - \int E ds = \int_a^c \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} Q /r^2 dr+ \int_c^{c+d} \frac{1}{k} \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} Q /r^2 dr + \int_{c+d}^b \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} Q /r^2 dr ##
And by using ##C = Q/V## We get an answer which is somehow large for writing here but It is just a bit of algebra after evaluating those integrals.
II) For this part I am not sure what should I use. If I say that ##E_{in ~dielectric} = \frac{1}{k} E_{without~dielectric} ## We get ##Q - Q' = Q/k## where Q' is induced charge. But I am not sure is it safe to use this equation in this part? The answer isn't in terms of ##r## radial distance.
##V = - \int E ds = \int_a^c \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} Q /r^2 dr+ \int_c^{c+d} \frac{1}{k} \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} Q /r^2 dr + \int_{c+d}^b \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} Q /r^2 dr ##
And by using ##C = Q/V## We get an answer which is somehow large for writing here but It is just a bit of algebra after evaluating those integrals.
II) For this part I am not sure what should I use. If I say that ##E_{in ~dielectric} = \frac{1}{k} E_{without~dielectric} ## We get ##Q - Q' = Q/k## where Q' is induced charge. But I am not sure is it safe to use this equation in this part? The answer isn't in terms of ##r## radial distance.