SUMMARY
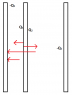
The discussion centers on the behavior of a middle metallic plate with charge Q placed between two other metallic plates at distances d1 and d2. The charge distribution on the outer plates is calculated as -Qd2/(d1+d2) and -Qd1/(d1+d2). The middle plate experiences forces due to the electric fields generated by the outer plates, leading to its movement towards the side with the greater distance (d2 > d1). The participants emphasize the importance of understanding electric fields and charge distributions, particularly in the context of capacitors and Gauss's law.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric fields and charge distributions
- Familiarity with Gauss's law and its applications
- Knowledge of capacitors and their behavior in electric circuits
- Concept of electrostatic induction and polarization in conductors
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of Gauss's law in electrostatics
- Learn about the behavior of capacitors, specifically parallel plate capacitors
- Explore the concept of charge-induced charge separation in conductors
- Investigate the effects of electric fields on metallic plates and their movement
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in understanding electrostatics and the behavior of charged conductors in electric fields.