Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around a combinatorial problem involving the arrangement of bulbs in a circuit powered by a battery. Participants explore how many distinct configurations can be created to light all the bulbs, considering various circuit topologies such as series and tree structures. The problem is framed within a mathematical context rather than an electrical one.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Mathematical reasoning, Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
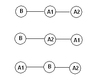
- One participant describes a circuit configuration involving a battery and multiple bulbs, asking how many ways the bulbs can be arranged to ensure they all light up.
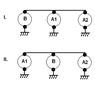
- Another participant questions whether the arrangement is limited to a single loop or if multiple loops are allowed, noting that this would significantly affect the number of configurations.
- A participant clarifies that the arrangement does not include loops, specifying that it can be either a tree or a series configuration.
- Some participants express confusion regarding the nature of the problem, with one suggesting that the answer could be infinite due to the lack of constraints on the battery or bulbs.
- Another participant emphasizes that the problem is mathematical, asserting that the battery's capacity is sufficient to light all bulbs.
- Several participants discuss the implications of treating the bulbs as distinct objects, leading to different combinatorial outcomes based on their arrangements.
- One participant proposes a systematic approach to calculate the number of topologically inequivalent graphs that can be formed with the bulbs, suggesting that graph theory may be applicable.
- Another participant mentions that for a series configuration, the number of arrangements could be calculated as (n+1)!/2, but notes that this only applies to series and that tree configurations would increase the total count.
- There is a suggestion to first determine the topology of the circuit before calculating permutations for each configuration.
- Some participants express uncertainty about the definitions and assumptions underlying the problem, particularly regarding the nature of the connections and the role of the battery.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the problem's parameters or the total number of configurations. Multiple competing views and interpretations of the circuit arrangements remain, with some participants focusing on series arrangements while others consider tree structures.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations in the discussion regarding the assumptions about the battery and bulb configurations, as well as the definitions of circuit types. The complexity of counting arrangements increases significantly with the number of bulbs, and participants acknowledge the difficulty in finding a general formula for larger n.