- #1
cvsanchez
- 9
- 0
Homework Statement
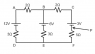
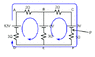
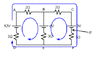
Find the potential difference at point P in the diagram.
Homework Equations
V=IR
ΣiVi=0
ΣIin=ΣIout
The Attempt at a Solution
I understand that you need to use Kirchoff's circuit laws to find the current and voltage at each resistor, but I can't comprehend how a current could flow at all since the positive and negative terminals are essentially isolated.
I haven't been able to find an example in my notes or textbook and nothing online clarified it.
My main problem is that I can't picture how any current "loops" could form in a circuit such as this one.