SUMMARY
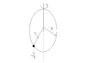
The discussion focuses on the dynamics of a bead on a frictionless vertical wire hoop of radius R, which rotates about a vertical axis with a period of revolution T. The key equation used is Fc = mv²/r, where Fc represents the required centripetal force. Participants emphasize the need to identify the forces acting on the bead, specifically the normal force N exerted by the wire and how it balances the gravitational force acting on the bead. The conversation highlights the importance of understanding the direction of acceleration to apply Newton's second law effectively.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of centripetal force and its calculation
- Familiarity with Newton's laws of motion
- Basic knowledge of rotational motion concepts
- Ability to analyze forces acting on objects in motion
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of centripetal force in rotating systems
- Learn about the applications of Newton's second law in circular motion
- Explore the effects of friction in rotational dynamics
- Investigate the relationship between period of revolution and angular velocity
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and circular motion, as well as educators seeking to clarify concepts related to forces in rotational systems.