Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around solving an initial value problem using various numerical methods: forward Euler, trapezoid, and backward Euler methods. Participants explore the implications of their results, particularly focusing on the graphical representations of the approximations for the expressions $(x^n)^2+(y^n)^2$ and the accuracy of each method.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Technical explanation, Debate/contested, Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Participants discuss the formulation of the backward Euler method and its implementation in code.
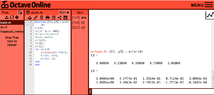
- Some participants suggest that the trapezoid method, being a second-order approximation, should yield smoother graphs compared to the first-order backward Euler method.
- There is uncertainty about the interpretation of the graphs, particularly regarding the smoothness of the red graph associated with the forward Euler method.
- Concerns are raised about the accuracy of the forward Euler method, with some participants suggesting it may not be exact enough due to the observed bends in the graph.
- Participants question why there is little difference between the trapezoid and backward Euler methods despite their differing orders of accuracy.
- Discussion includes the relationship between the smoothness of the graph and the continuity of derivatives, particularly in relation to the presence of bends in the graph.
- Some participants express confusion about the implications of discontinuities in derivatives and their effects on the graphical representations of the solutions.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the implications of the graphical results or the reasons behind the observed behaviors of the different methods. Multiple competing views remain regarding the accuracy and smoothness of the methods discussed.
Contextual Notes
Participants express uncertainty about the exact nature of the graphs and the mathematical properties of the solutions, including continuity and differentiability of the derivatives involved.
Who May Find This Useful
Readers interested in numerical methods for solving differential equations, particularly those studying initial value problems and their graphical interpretations.