- #1
Boxlife27
- 12
- 0
~~Conceptual Normal Force Question~~
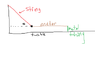
Hello! Suppose there is a meter stick suspended from and parallel to a table. On one end, the meter stick is held up by a piece of string at an angle. On the other end, the meter stick is held up by a metal thing about 10cm tall, simply allowing the stick to rest upon it. Remember, the meter stick is parallel to the ground... How would one find the normal force exerted by the metal thing that the meter stick is resting upon? Thank you very much
Hello! Suppose there is a meter stick suspended from and parallel to a table. On one end, the meter stick is held up by a piece of string at an angle. On the other end, the meter stick is held up by a metal thing about 10cm tall, simply allowing the stick to rest upon it. Remember, the meter stick is parallel to the ground... How would one find the normal force exerted by the metal thing that the meter stick is resting upon? Thank you very much