- #1
sd34
- 9
- 0
Please post this type of questions in the homework section, filling the template.
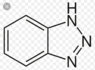
I have the following molecule: benzotriazole. It has pka=12. At pH=6 which form prevails?
a) neutral
b) anionic
c) cationic
d) none of the above.
I thought the correct answer was c) cationic: pH<pka, benzotriazole has basic functional groups (amines).
a) neutral
b) anionic
c) cationic
d) none of the above.
I thought the correct answer was c) cationic: pH<pka, benzotriazole has basic functional groups (amines).
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: