SUMMARY
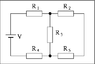
The discussion focuses on calculating the equivalent resistance and current through a resistor in an electric circuit with a voltage of 21.7 V and resistors R1 to R5, each valued at 6.00 Ohm. The equivalent resistance of the circuit is determined to be 16 Ohm. The total current flowing through the circuit is calculated to be 1.35625 A, leading to the inquiry about the current specifically through resistor R4. Participants clarify that the current through R4 is equal to the total current from the battery due to the series and parallel configurations of the resistors.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law
- Knowledge of series and parallel resistor combinations
- Familiarity with basic circuit analysis techniques
- Ability to interpret circuit diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of series and parallel circuits in detail
- Learn how to apply Kirchhoff's laws for circuit analysis
- Explore the concept of current division in parallel circuits
- Investigate the impact of resistor values on total circuit current
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electrical engineering, educators teaching circuit analysis, and hobbyists interested in understanding electric circuits and resistor behavior.