shivajikobardan
- 637
- 54
- Homework Statement
- Why is data sharing not possible in traditional file system(TFS) (vs DBMS)?
- Relevant Equations
- None
I know data is decentralized in TFS. But how does that makes data sharing difficult?
We've got distributed computing for the similar purpose on different machines as well.
I read a lot on this but failed to find any information regarding why it was not possible to share data in TFS as compared to DBMS? And why is it easy to share data in DBMS?
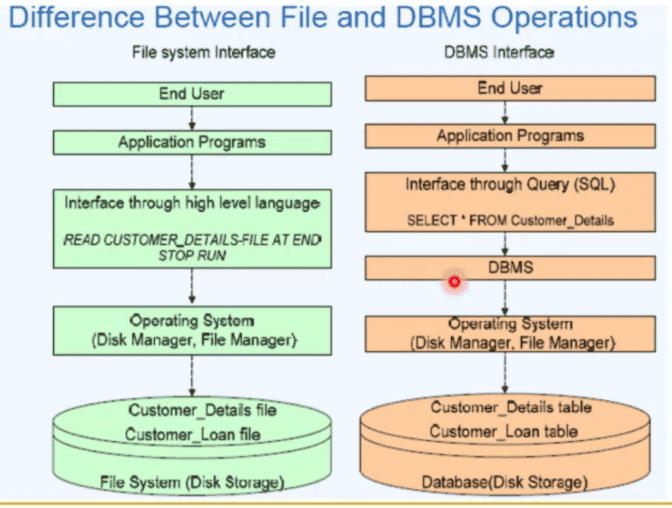
Source: Parteek Bhatia "Simplified Approach to DBMS"
According to this figure, I really don't see anything not offered in TFS that is offered in DBMS.
We've got distributed computing for the similar purpose on different machines as well.
I read a lot on this but failed to find any information regarding why it was not possible to share data in TFS as compared to DBMS? And why is it easy to share data in DBMS?
Source: Parteek Bhatia "Simplified Approach to DBMS"
According to this figure, I really don't see anything not offered in TFS that is offered in DBMS.