Discussion Overview
The discussion centers on the differences between DC and AC resistance in diode systems, exploring the concepts of bulk resistance and dynamic resistance as they relate to current-voltage (I-V) characteristics. Participants examine the implications of these resistances in both theoretical and practical contexts, including small signal AC amplifiers.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
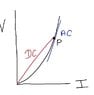
- Some participants express confusion regarding the distinction between DC and AC resistance, particularly in diode systems, noting that DC resistance is derived from specific I-V points while AC resistance involves changes in current and voltage.
- One participant explains that DC resistance is calculated as R = V/I at a specific operating point, while AC resistance is defined by the slope of the I-V curve, indicating how the diode responds to small changes in current.
- Another participant highlights that resistance is not constant and varies with applied voltage and temperature, suggesting that algebraic expressions may clarify these relationships better than verbal explanations.
- Some participants question why DC resistance does not approximate AC resistance closely, noting that different methods (approximation for DC and calculus for AC) are used in their derivations.
- Clarifications are made regarding the "third approximation" of diodes, which treats the diode as a switch and resistor above a certain threshold voltage, affecting the understanding of bulk resistance.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the definitions and implications of DC and AC resistance but express differing views on the relationship between the two and the methods used to derive them. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the extent to which DC resistance can approximate AC resistance.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include the dependence on specific operating points for DC resistance and the assumptions made in approximating diode behavior. The discussion also highlights the complexity of I-V characteristics in non-linear devices.