SUMMARY
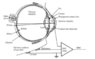
The discussion focuses on designing a system to measure the electroretinogram (ERG) using differential amplifiers and appropriate electrode placement. Key components include placing one ERG electrode on the cornea and another on the patient's body for reference, with a ground electrode attached to the forehead. Participants emphasize the importance of selecting the desired sampling rate based on signal bandwidth, designing the differential amplifier circuit, and incorporating anti-alias filters. Additionally, they suggest studying ECG and EEG measurement systems for similar design components.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of differential amplifier design for biomedical applications
- Knowledge of electrode placement and reference connections in ERG measurement
- Familiarity with anti-alias filters and their design
- Basic principles of signal bandwidth and sampling rates
NEXT STEPS
- Research differential amplifier circuit design for biomedical applications
- Learn about anti-alias filter design techniques and component selection
- Study the principles of sampling rate selection based on signal bandwidth
- Explore ECG and EEG measurement systems for comparative analysis
USEFUL FOR
Biomedical engineers, electrical engineers, and researchers involved in designing and implementing electroretinogram measurement systems.