SUMMARY
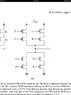
The discussion focuses on designing a 2-input XOR gate with specific parameters: RL = 1KΩ, VDD = 1.8V, VOL = 0.1V, and VOH = 1.7V. Participants emphasize the importance of considering the transistor characteristics, particularly the ON resistance and current sourcing capabilities, to ensure the output voltage meets the logic level requirements. The equations provided for triode and cutoff regions are crucial for understanding the transistor operation in this design context. The conversation highlights the need for clarity on whether the design should focus on generic transistor implementation or detailed transistor design.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of MOSFET operation and characteristics
- Familiarity with digital logic design principles
- Knowledge of voltage levels in digital circuits
- Basic proficiency in circuit analysis techniques
NEXT STEPS
- Study MOSFET characteristics and how they affect circuit design
- Learn about voltage divider principles in digital circuits
- Research the design of logic gates using CMOS technology
- Explore simulation tools for testing transistor-level designs
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and students studying digital electronics who are involved in designing logic gates and understanding transistor behavior in circuit applications.